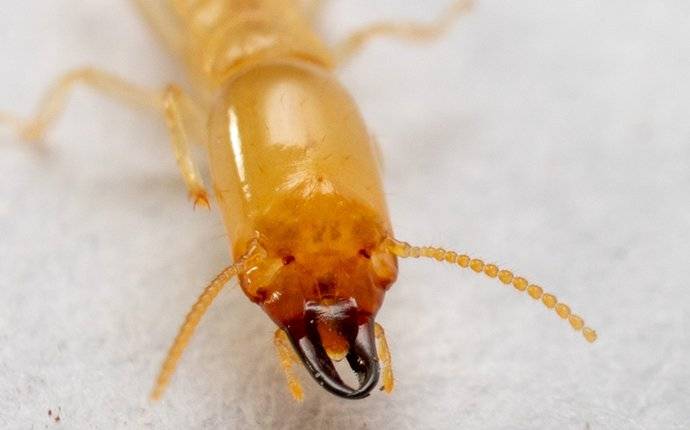
Termites do not bite people. They are not known to threaten humans directly and do not have mouthparts adapted for biting or stinging.
You might be afraid that the termites might bite you when you hear the misconception about the termite’s behavior. Besides, you might inquire regarding the aggressive behavior of termites for the following reasons,
- Fear of property damage.
- Concerns about treatment costs.
- Worry about the inconvenience of an infestation.
- Fear of potential health hazards.
- Anxiety over the unknown and uncontrollable nature of infestations.
Whatever the reason is, if you want to learn about the termite’s biting mechanisms and the potential inconvenience that the termite causes, keep reading on.
Understanding Termite Biting Mechanisms:
Termites, in general, do not bite people in the way that some other insects do. Let’s delve into the details to understand why:
Termite mandibles and their primary purpose
Termites have mandibles, which are specialized mouthparts designed for chewing and processing cellulose-rich materials like wood, plant fibers, and other organic matter.
Their primary purpose is to break down and digest cellulose to obtain nutrients for the termite colony.
Differentiating between termite biting and human skin irritation
Termite mandibles are adapted for their specific diet and cannot inflict bites on humans in the same way that, for example, mosquitoes or bedbugs do.
Termite mandibles are not designed for piercing human skin and are not equipped with the structures necessary to puncture or feed on human blood.
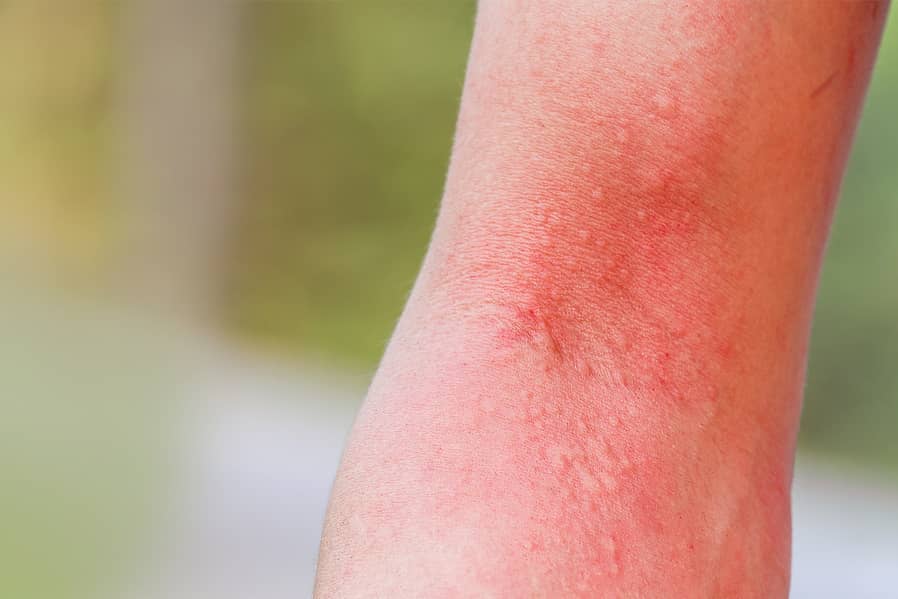
However, there can be instances of termite-related irritation in humans. When termites are disturbed or threatened, they may release defensive secretions.
These secretions can contain chemical compounds that are responsible for skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
In summary, while termites have mandibles designed for chewing cellulose, they do not bite people in the traditional sense.
Any skin irritation caused by termites is more likely to be a result of contact with their defensive secretions rather than a deliberate biting action.
Termite Species and Their Interactions with Humans:
Let’s explore the interaction between humans and different termite species to determine if termites bite people:
Termite species are commonly found near human habitats
Several termite species are commonly found near human habitats. These include:
Subterranean Termites: These common termite species live in underground colonies and create mud tubes to reach their food sources, often including wooden structures in homes.
Drywood Termites: Drywood termites live in dry wood and don’t rely on soil contact. They make their colonies inside the wood they eat.
Dampwood Termites: Dampwood termites are typically found in damp or decaying wood, such as fallen trees or rotting logs. They are less likely to infest human structures.
The likelihood of termites biting humans:
Termites, in general, do not bite humans as a primary behavior. Their mandibles are adapted for processing cellulose-based materials and lack the specialized mouthparts necessary for biting or feeding on humans.
However, there can be rare situations where termites may come into contact with humans, leading to minor irritation. For example:
Defensive Behavior: When termites are disturbed or threatened, they may release defensive secretions. These secretions can contain chemical compounds that may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions
This can be mistaken for a “bite,” but it’s a reaction to the termite’s defensive chemicals rather than a deliberate act of biting.
Accidental Contact: Occasionally, termites may contact a person’s skin or clothing. Such encounters are typically unexpected and do not involve aggressive biting behavior.
In summary, while termites do not bite humans as part of their natural behavior, minor skin irritation can occur when humans come into contact with defensive secretions or accidentally encounter termites.
However, these occurrences are relatively rare, and termites are not considered a direct threat to human health in terms of biting or feeding on humans.
Potential Inconveniences Caused by Termites
Termites don’t typically bite people. Let’s delve into why:
Destructive Behavior Caused by Termites:
Termites are known for their destructive habits, but their primary target isn’t humans. Instead, they have a voracious appetite for wood and cellulose materials found in structures like houses and trees.
These tiny insects can silently feast on wooden structures, causing significant damage over time.
How Termite Bites Are Usually a Secondary Concern:
Termites’ Diet: Termites are herbivores. They mainly feed on cellulose, which is abundant in wood, plants, and paper. Their mouthparts are adapted for breaking down cellulose, making it difficult for them to bite humans.
Size and Anatomy: Termites are small, often less than half an inch long, and their mandibles are designed for chewing through wood fibers, not for biting human skin. They lack the biting apparatus many other insects possess, like mosquitoes or ants.
Non-Aggressive Nature: Termites are not aggressive toward humans. They are primarily interested in their wood-based meals and don’t perceive humans as a food source or threat. They are, in fact, quite shy and tend to avoid interaction with people.
Rare Incidents: While extremely rare, there have been cases where termites have bitten humans, but these incidents are more accidental than intentional. It usually occurs when a termite is inadvertently trapped against the skin or feels threatened.
Even in such cases, termite bites are virtually painless and do not pose any significant health risks.
In conclusion, termites are not known for biting people, as their biology and behavior are geared towards consuming cellulose-rich materials.
The damage they inflict on wooden structures is their primary concern, and any potential interaction with humans is typically harmless and accidental.
Allergic Reactions to Termite Bites
When it comes to termite bites, it’s essential to know about possible allergic reactions, even though they are quite rare.
Possible Allergic Reactions Caused by Termite Bites:
Allergic Sensitivity: Some individuals may be generally allergic to insect bites, including termite bites. When a person with this sensitivity is bitten, they might experience an allergic reaction.
Symptoms: Allergic reactions to termite bites can manifest as redness, itching, swelling, and discomfort around the bite area. In severe cases, symptoms can include trouble breathing, hives, or even anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
The Rarity of Severe Allergic Reactions:
Low Incidence: It’s important to emphasize that severe allergic reactions to termite bites are extremely rare. Most people who termites bite, if it happens at all, experience mild irritation that subsides without any lasting effects.
Comparison to Other Insects: When it comes to insect bites, termites are not among the most common culprits for severe allergic reactions. In contrast, stinging insects like bees and wasps are more likely to cause severe allergic responses.
Preventive Measures: To reduce the risk of allergic reactions, avoiding provoking termites and taking precautions like wearing protective clothing when dealing with infestations is advisable. Individuals should always carry prescribed epinephrine (EpiPen) to counteract severe allergic responses in cases of known insect allergies.
In summary, while allergic reactions to termite bites are possible, they are exceptionally rare.
Most termite bites result in minor irritation, and severe allergic reactions are more commonly associated with other insects.
It’s essential to be aware of these possibilities but also important to remember that the likelihood of a severe reaction to a termite bite is quite low.
Prevention and Control Methods

Tips for Minimizing Termite Infestations in Homes and Structures:
Maintain Dry Conditions: Termites are attracted to moisture. Ensure that your home’s foundation, roof, and plumbing are free from leaks and water damage. Fix any leaks promptly.
Remove Wood-to-Ground Contact: Avoid direct contact between soil and wood in your home’s structure. Use concrete or metal barriers to prevent termites from easily accessing wood.
Store Firewood Away: If you have firewood, store it at a distance from your home. Termites can easily move from wood piles to your house.
Regularly Inspect Wood: Periodically inspect wooden components of your home, such as beams, frames, and foundations, for any signs of termite damage.
Use Termite-Resistant Materials: When building or renovating, think about using termite-resistant materials or treated wood.
Importance of Regular Termite Inspections and Professional Assistance:
Early Detection: Regular inspections by professionals can catch termite infestations early before they cause extensive damage. This can save you significant money in repairs.
Effective Treatment: If termites are detected, professionals can recommend and carry out effective treatments, such as baiting systems or chemical barriers, to eliminate the infestation.
Preventive Measures: Pest control experts can also provide ongoing preventive treatments to protect your home from future infestations.
Knowledge and Expertise: Professionals have the knowledge and tools to identify different termite species and their specific behaviors, which is crucial for effective control.
Legal Compliance: In some areas, regular termite inspections may be required by law when selling or buying a home.
FAQs
Can termites cause skin irritation or allergic reactions?
Yes, Termites can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals due to contact with termite saliva, feces, or shed exoskeletons. However, such cases are rare.
Are termite bites painful?
No, termite bites aren’t painful, as they do not bite in the same way that insects like mosquitoes or bed bugs do, so they do not cause the typical pain associated with insect bites.
Do termites bite pets?
No, Termites are unlikely to bite pets, as they do not seek out animals for blood meals; their primary focus is on cellulose-based materials.
Can termites damage wooden structures and furniture?
Yes, termites can damage wooden structures and furniture by feeding on cellulose materials.
What are the signs of a termite infestation?
Signs of termite infestations include damaged wood, mud tubes, dropped wings (from swarmer termites), and the presence of termite workers or soldiers.
Are there any health risks associated with termite infestations?
No, there are no direct health risks associated with termite infestations, Yet they can result in costly structural damage.
How do you prevent termite infestations?
Prevent infestations by reducing moisture around your property, sealing entry points, and scheduling regular termite inspections.
Are there natural ways to repel termites?
Yes, some natural remedies to repel termites, like using nematodes or orange oil, may help deter termites, but professional treatment is often necessary for effective control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, termites are not known to bite people. They primarily feed on wood and cellulose materials, posing minimal risk to humans.
While they may have mandibles, they are not designed for biting humans. This reassurance should alleviate concerns and highlight that termite prevention and control strategies primarily focus on protecting properties rather than human safety.

